|
| An infographic about infographics - click to enlarge |
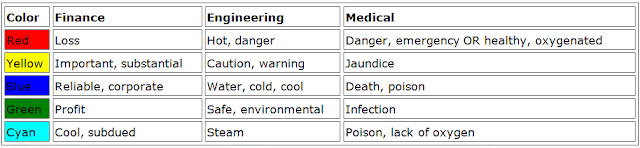
Colour Theory Infographic
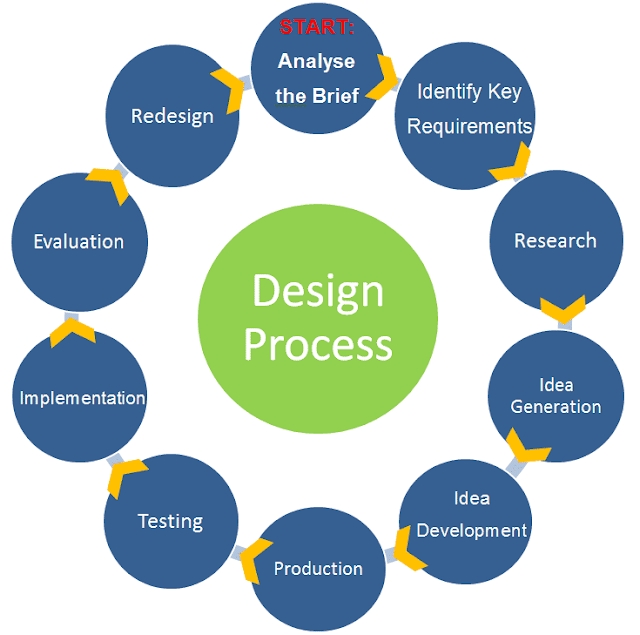
Design Process Infographic
The design process is the single most important piece of design theory that a designer needs to know. This design infographic outlines the stages of the design process and the order in which they are to be completed. It also highlights that design can be a cyclical process which is in constant evolution. If you want to know more about each stage of the design process then you can read more >>>
Design Careers Infographic
| Careers in Design infographic - click to enlarge |
This handy little infographic is from photoshop-plus.co.uk and it outlines some of the main careers in the design area and the salaries available to designers. However the design of the infographic itself can also be used as an educational tool for design students as it's clean and crisp layout combined with the bright colours of each elements contrasting nicely with the light grey background. Click on any of these links to learn more about a career in web design, interior design, graphic design, games design or furniture design.
The Elements of Design Infographic
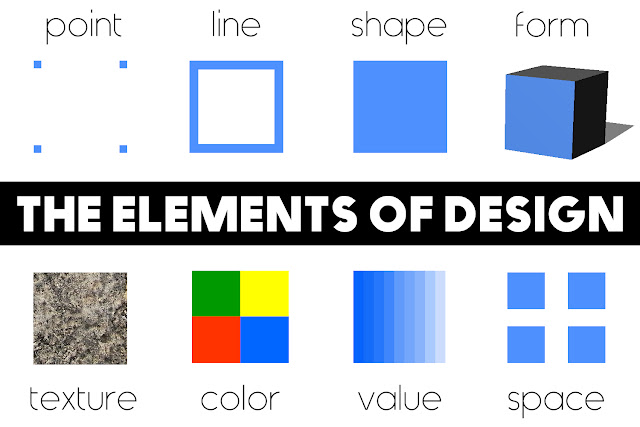 |
| The elements of design - click to enlarge |
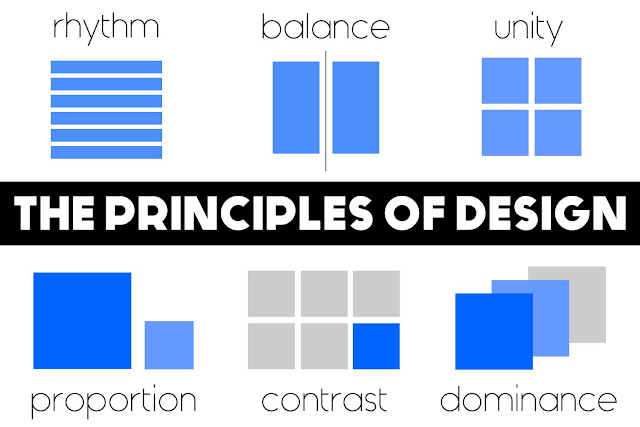
The Principles Of Design
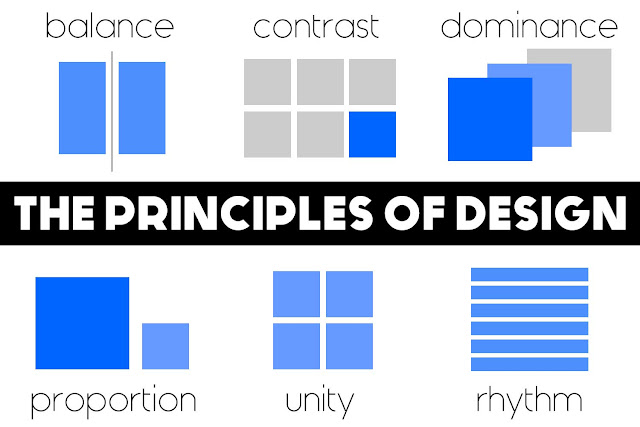 |
| The principles of design - click to enlarge |
The design infographic above simultaneously lists and explains the 6 basic concepts or theories in the area of design, collectively known as the principles of design. They are Balance (Alignment), Rhythm (Repetition), Proportion (Proximity), Dominance (Emphasis) Unity (Harmony) and Contrast. Theses principles are sometimes know by different names hence the brackets.They represent the basic rules of how to arrange a composition and create a successful design. In order words they guide us in the way we arrange the elements of design. Sometimes we look at an image or object and we find it aesthetically pleasing or easy on the eye but we may not quite understand why - the reason is that one or more of the principles of design are at work. If you would like to learn more about each of the principles of design you can read more >>>