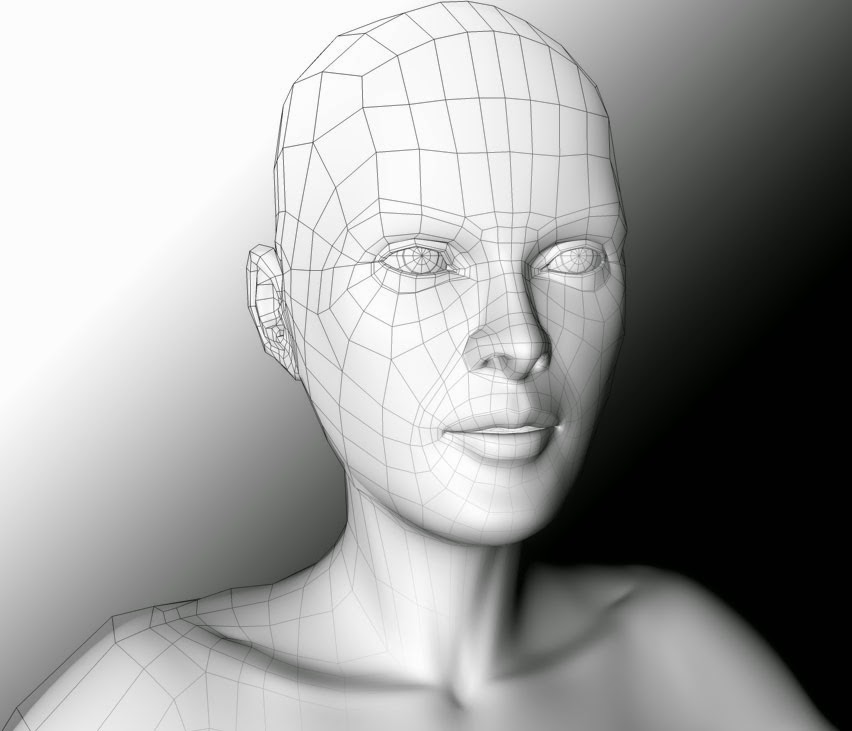
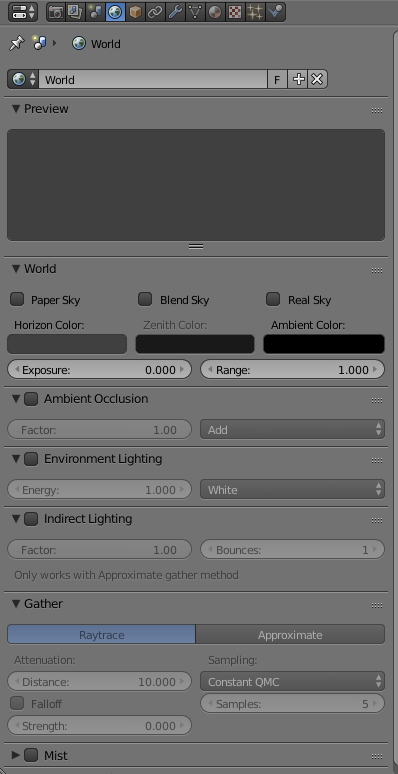
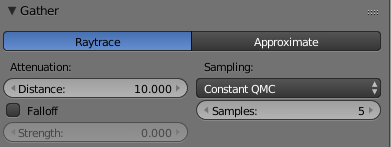
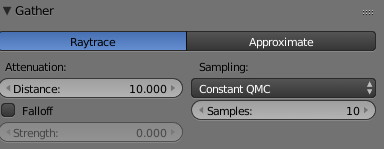
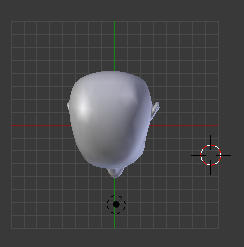
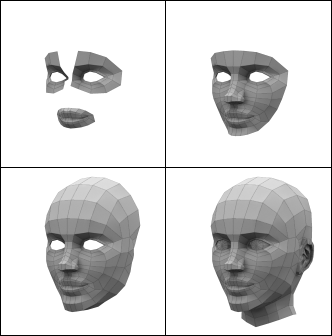
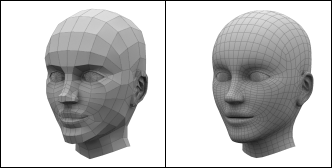
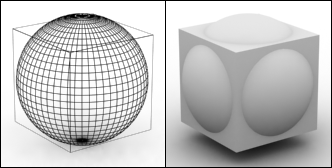
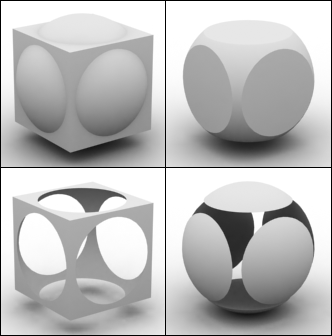
These series of updated articles aim to provide you with everything you need to know about on 3D modelling and graphics. In 3D graphics, elements are visualized by creating three-dimensional models out of them. The final image is rendered from a virtual scene that utilizes several elements which are familiar from real life such as lights, materials and cameras. 3D graphics can be seen in multiple different forms such as an image, an animation or real time visualization inside of a computer game. If you are interested in a career in animation or gaming then this series is especially relevant for you!
We recommend reading this articles in the order presented if you are a beginner, however they are designed in such as way as that they are relatively independent of each other.
The creation of 3D graphics is a complicated process and therefore is, in my opinion, easier to understand when discussed in small pieces, hence this 8 article series. we hope that you find it useful and as always we welcome your feedback.
We recommend reading this articles in the order presented if you are a beginner, however they are designed in such as way as that they are relatively independent of each other.
Select an area of 3D modelling to get started...
The creation of 3D graphics is a complicated process and therefore is, in my opinion, easier to understand when discussed in small pieces, hence this 8 article series. we hope that you find it useful and as always we welcome your feedback.