|
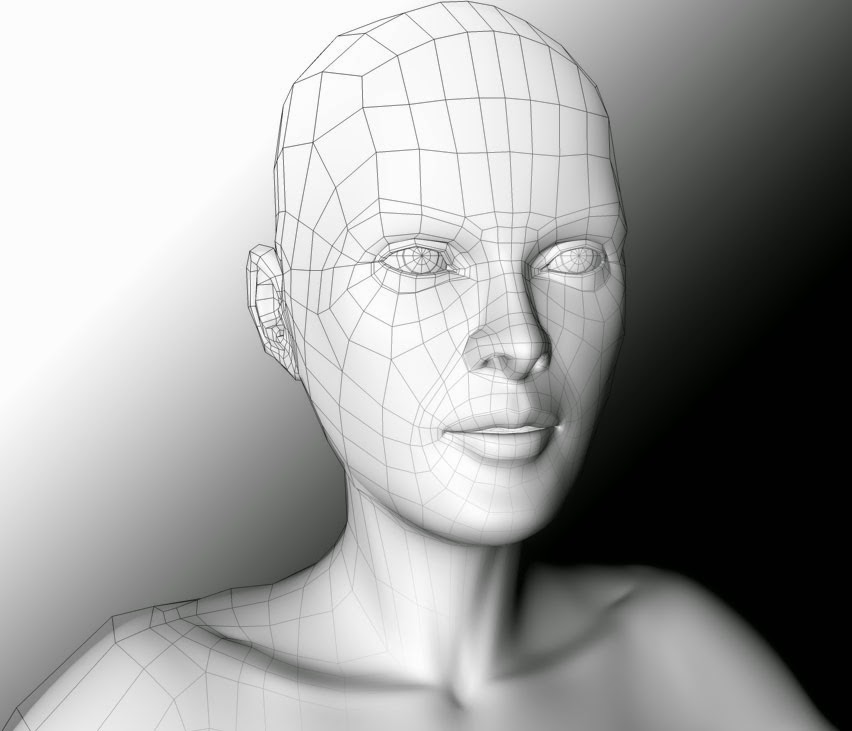
| 3D Modelling Software Screenshot |
The creation of 3D graphics is a complicated process and therefore is, in my opinion, easier to understand when discussed in small pieces, hence the 5 article series. First up it's 3D Modelling which refers to the creation of the 3D model itself.
3D Modelling - The Parts...
A 3D model is a mathematical representation of an object. 3D modelling can be compared to sculpting. Artist builds or moulds a 3D object by taking into account all different sides and angles. 3D models consist of smaller elements (vertex, edge, face, polygon) which can be manipulated individually in whatever software you are using to model your 3D object, such as Blender, Maya or 3D Studio Max.
Vertex:
 |
| vertex |
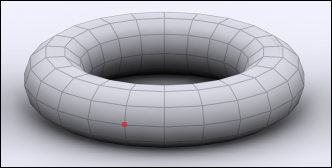
Edge:
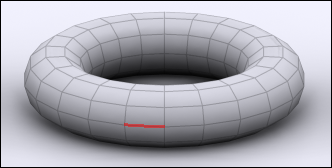 |
| edge |
Face:
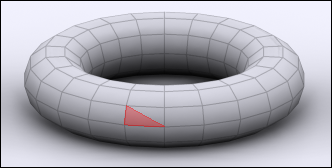 |
| face |
Face is a triangle. Face is a surface between three corner vertices and three surrounding edges. Transforming a face affects all connected vertices, edges and polygons.
Polygon:
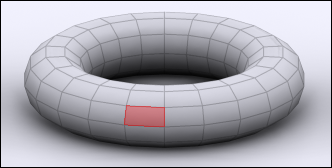 |
| polygon |
Polygon is an even surface which has four or more corners and is made of two or more faces. A polygon is surrounded by edges and has a vertex in each corner. Animated high quality 3D characters are often made mostly of four-sided polygons. Polygons with 5 or more sides can cause problems in deforming surfaces such as a human face.
3D Modelling - The Techniques...
Standard Primitives and Modifiers:
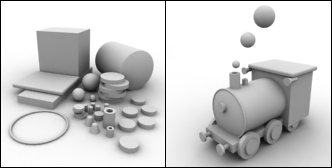 |
| Primitives and Modifiers |
Many 3D software packages include tools for creating standard objects such as boxes and spheres easily. One of the simplest 3D modelling techniques is to combine these standard objects to create complex 3D models. 3D Studio MAX includes standard objects such as sphere, cube and tube. These standard objects can be modified through their parameters (radius, height etc.) or through special modifiers (stretch, bend etc.). By combining several different standard objects and by modifying them, one can create complex 3D models.
Polygon Modelling:
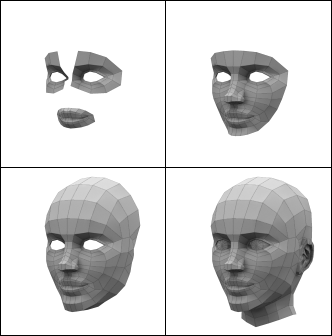 |
| Stages of Polygon Modelling |
Complex objects are often modeled polygon by polygon. 3D software packages include many efficient tools for creating and manipulating polygons.
Subdivision surface means a surface which is created by dividing the original 3D model into smaller polygons. At the same time 3D model's corners become rounder and the surface becomes smoother. Subdivision surfaces is a very popular modelling technique. The advantage of a subdivision surface is the fact that one can create a coarse 3D model which is then automatically subdivided into a smoother surface.
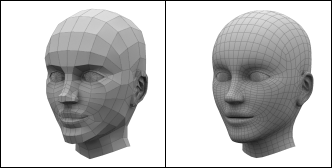 |
| A Polygon Model Before and After Subdivision |
Boolean Operations:
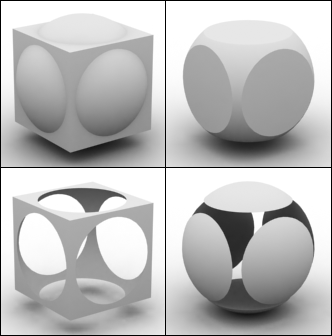 |
| The 4 Possible Outcomes of a Boolean Operation |
- Union: Two 3D models are combined and the unnecessary geometry inside of the Models is removed.
- Intersection: Overlapping a part of the two 3D objects.
- Subtraction (A-B): Object A is subtracted from object B.
- Subtraction (B-A): Object B is subtracted from object A.
NURBS:
Solid of Revolution:
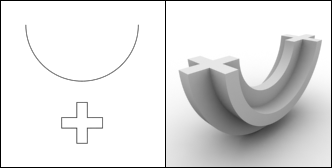 |
| A cross section and the object created by a solid of revolution |
Lines:
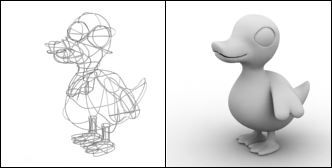 |
| A 3D object and the cage of lines used to create it |